逆向-安卓环境下的检测
🤓5ea1
调用root限定指令
在root后的设备中往往可以使用su来提升用户的权限,那么可以借助process来在app中调用su类似的指令,然后通过读取返回的报错信息或返回的回显,来判断是否是root用户,当然,在不同防护策略下,这种判断方式可能会出现意想不到的错误
su
public static boolean isRoot_su() {
boolean Root;
try {
//启动指令进程
ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder("su");
pb.redirectErrorStream(true); // 将错误流和输出流合并
Process process = pb.start();
//从流数据中读取
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String Line;
while( (Line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
Log.d("MyT0ols",Line);
}
Root=true;
}
catch (IOException e) {
Root=false;
}
return Root;
}
ProcessBuilder创建shell指令进程
一般而言,只有root后的设备才能调用su命令(即执行/bin/su)来获取权限,但是有些非root设备中也会包含这个文件,但不允许使用,或是某些root设备不允许使用su指令,这使得这种方法相对而言不太稳定
which su
public static boolean isRoot_which() {
boolean Root = false;
//throw new RuntimeException("Test crash to check if method is called");
Log.d("seal", "which output: ");
try {
//启动指令进程
ProcessBuilder pb = new ProcessBuilder("which", "su");
pb.redirectErrorStream(true);
Process process = pb.start();
//输出缓存区
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
Log.d("seal", "which output: " + line);
}
//直接获取回显码
try {
int exitCode = process.waitFor();
Log.d("seal",String.valueOf(exitCode));
if(exitCode == 0) {
Log.d("MainActivity","ROOT!");
Root = true;
}
else {
Root = false;
}
}
catch ( InterruptedException e) {
Root = false;
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
Root = false;
}
Log.d("seal", "which output: ");
return Root;
}
和上面的大致相同,但是由于需要读取exitcode,所以需要先输出缓冲区中的数据,否则会卡死
在测试第二种方法的时候,我发现HUAWEI设备会出现一些耐人寻味的问题,它会追踪我的which su进程,将其定义为病毒,并hook我的测试应用,导致检查错误
判定指定文件夹是否可读写
读取特定android属性
检索已安装目录下有没有相关提权应用
Since the protection of the application sandbox has been more stringent in Android 11 and above. We need to declare what we want to do in the AndroidManifest.xml
P.S. Use this command can list all the apps which is visibal
adb shell pm list packages -3 -e | grep -v "android.permission.LAUNCHER"
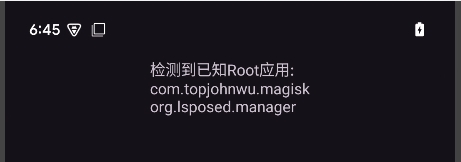
I selected these specific applications to test below.
String[] applist = {
"com.topjohnwu.magisk", // Magisk (The most popular)
"eu.chainfire.supersu", // SuperSU (popular before)
"com.supersu", // SuperSU (old)
"com.kingroot.kinguser", // KingRoot
"com.kingo.root", // KingoRoot
"com.kingroot.RushRoot", // KingRoot class
"com.joeykrim.rootcheck", // Root Checker
"com.burrowsapps.rootchecker", // Root Checker
"de.robv.android.xposed.installer",// Xposed Installer
"org.lsposed.manager", // LSPosed Manager
"stericson.busybox", // BusyBox
"jackpal.androidterm", // Terminal Emulator
"com.termux", // Termux
"com.speedsoftware.rootexplorer", // Root Explorer
"com.ghisler.android.TotalCommander", // Total Commander (Root permission)
"pl.solidexplorer2", // Solid Explorer (Root permission)
};
In this way ,there are kind of ways to bypass
- Because we just use fixed package names and fixed keywords, so we can change the apps' package name accroding to the fixed data in the detecting function
- We can also use frida to hook the check function, which can solve the question fundamentally
Java.perform(function () {
console.log("[*] Frida 脚本已加载!");
try {
const MainActivity = Java.use("com.seal.localdetect.MainActivity");
const AppDetect = Java.use("com.seal.localdetect.AppDetect");
const JavaString = Java.use("java.lang.String");
MainActivity.main.implementation = function () {
console.log("[*] MainActivity.main() 方法被 Hook 了!");
let detectedAppName1 = AppDetect.hasListedApps(this);
console.log("[JS] AppDetect.hasListedApps() 返回: " + detectedAppName1);
if (this.textView1.value != null) {
if (detectedAppName1 != null) {
const message1 = "检测到已知Root应用: " + detectedAppName1.toString();
this.textView1.value.setText(JavaString.$new("一切正常(并非"));
console.log("[*] 已更新 textView1 的文本内容: " + message1);
} else {
this.textView1.value.setText(JavaString.$new("未检测到已知Root应用。"));
console.log("[*] 已更新 textView1 的文本内容: " + message1);
}
} else {
console.log("[!] textView1 未初始化!");
}
let detectedAppName2 = AppDetect.hasExtendedApps(this);
console.log("[JS] AppDetect.hasExtendedApps() 返回: " + detectedAppName2);
if (this.textView2.value != null) {
if (detectedAppName2 != null) {
const message2 = "检测到已知Root应用: " + detectedAppName2.toString();
this.textView2.value.setText(JavaString.$new("一切正常(并非"));
console.log("[*] 已更新 textView2 的文本内容: " + message2);
} else {
this.textView2.value.setText(JavaString.$new("未检测到已知Root应用。"));
console.log("[*] 已更新 textView2 的文本内容: " + message2);
}
} else {
console.log("[!] textView2 未初始化!");
}
};
console.log("[*] MainActivity.main() Hook 设置成功!");
} catch (e) {
console.error("[!] Hook 过程中出现错误:", e.stack);
}
});
here is a way to hook what i need .Though hook the AppDetect Function is clearly a better way, but i choose to hook main finally.
When hooking, i found some problems —— first ,while i use implementation to change the logic in main, there are many difference between js and java ,so i need to use some other data types to place such as String and StringBuffer